 Special Authority.
Special Authority. Religious, Cultural, and Other Considerations.
Religious, Cultural, and Other Considerations.
|
✔ |
✘ |
Reason: |
|
|
10 mg |
10mg |
10mg may look like 100g |
|
|
2 mg |
2.0 mg |
2.0 mg may look like 20 mg |
|
|
0.5 mg |
.5 mg |
.5 mg may look like 5 mg |
|
|
UNIT(S) |
U or u |
U may look like 0 |
|
|
MICROGRAMS |
μg, mcg |
μg may look like mg |
|
|
ONCE DAILY |
OD, D or QD |
od may look like bd, d may look like 1d (1 dose), qd may look like qid (4 times a day) |
|
|
NANOGRAM |
ng |
ng could be mistaken for mg |
|
|
MILLIMOLE or MMOL |
milliequivalent or mEq |
milliequivalent could be confused with millimole |
|
|
SUBLINGUAL |
SL |
SL could be mistaken for SC |
|
|
SUBCUT |
SC |
SC could be mistaken for SL |
|
|
QID |
QDS |
qds could be mistaken for daily |
|
|
L |
l |
I could be mistaken for 1 (one) |
|
|
The following Latin and other abbreviations are acceptable: |
|||
|
BD |
= twice daily |
IM |
= intramuscular |
|
Q"X"H |
= every "x" hours |
IV |
= intravenous |
|
PRN |
= as required |
SUBCUT |
= subcutaneously |
|
TDS |
= three times a day |
PO |
= oral |
|
QID |
= four times a day |
PR |
= rectal |
|
MANE |
= in the morning |
TOP |
= topical |
|
NOCTE |
= at night |
INH |
= inhaled |
 Medicine Use Outside Hospital Medicines List Restrictions (Non-HML NPPA).
Medicine Use Outside Hospital Medicines List Restrictions (Non-HML NPPA).Enter and/or update adverse drug reactions (Allergies and Intolerances box) on MedChart.
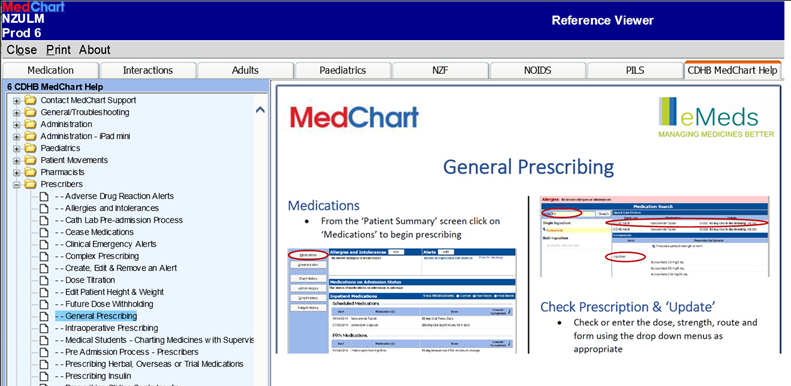
Enter and/or update adverse drug reactions (Drug Reactions box) on National Medication Charts.
 this guidance if using medicines not on the HML (including Named Patient Pharmaceutical Assessment (NPPA)).
this guidance if using medicines not on the HML (including Named Patient Pharmaceutical Assessment (NPPA)).Discharge prescribing is part of the writing of the discharge summary, in Health Connect South.
See Writing Discharge Summaries – Hints and Tips on Hospital HealthPathways.
 Pharmacies outside of HNZ Canterbury.
Pharmacies outside of HNZ Canterbury. Hospital supply of medications to use in the community.
Hospital supply of medications to use in the community. Controlled Drugs (CD) prescribing summary.
Controlled Drugs (CD) prescribing summary. Controlled drugs written on a triplicate-controlled drug prescription form H572.
Controlled drugs written on a triplicate-controlled drug prescription form H572. Controlled drugs written electronically and delivered to the patient's pharmacy via ERMS.
Controlled drugs written electronically and delivered to the patient's pharmacy via ERMS. Special Authority.
Special Authority. contact the Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy (OPAT) Service via the Infection Management Service on 027 702 4268 or via the switchboard.
contact the Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy (OPAT) Service via the Infection Management Service on 027 702 4268 or via the switchboard.In addition to the general advice above, contact the patient's community pharmacy:
Funding:
Supply of hospital medicines to take home after hours:
Special circumstances:
Topic Code: 132290